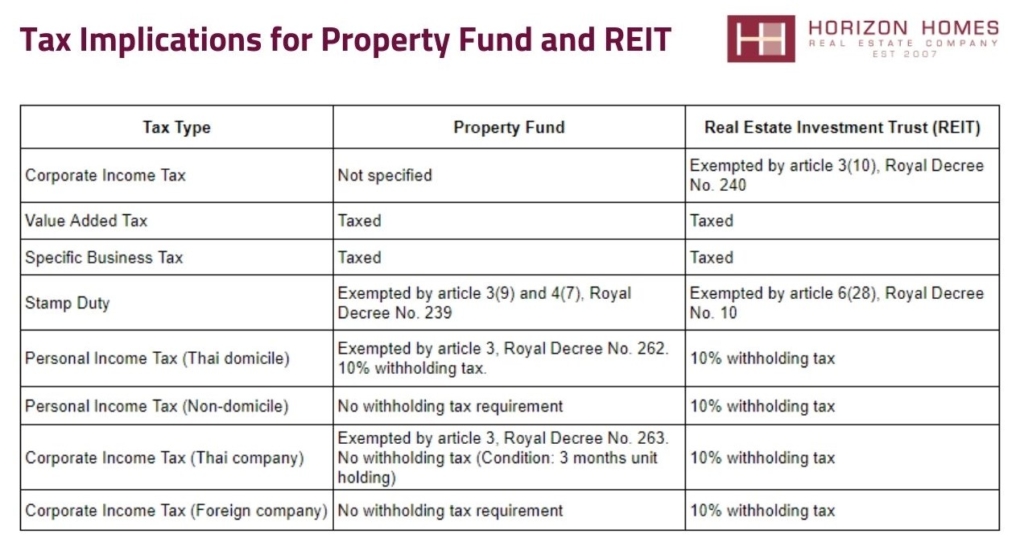
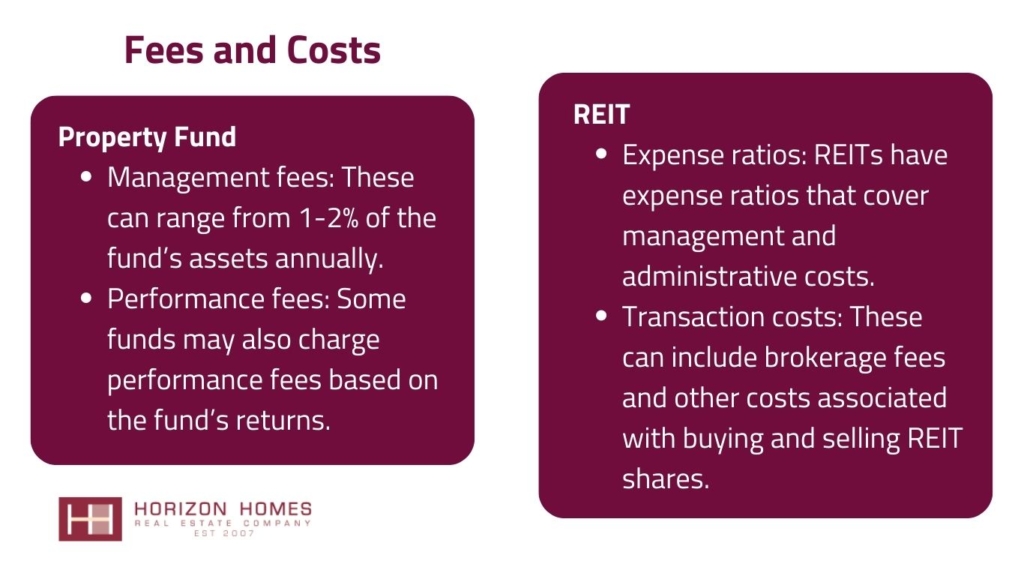
Property Funds are collective investment schemes that pool capital from multiple investors to purchase, manage, and sell real estate properties. REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate across a range of property sectors. Understanding the differences between these two investment vehicles is crucial for making informed decisions in real estate investing.
What is a Property Fund?
Property funds are investment vehicles that pool capital from multiple investors to acquire and manage real estate assets. Their primary purpose is to provide individuals with an opportunity to participate in real estate investment without needing significant capital or expertise.
There are two main types of property funds: closed-end funds and open-end funds. Closed-end funds issue a fixed number of shares and trade on stock exchanges, allowing for liquidity at market prices. In contrast, open-end funds continuously issue and redeem shares based on investor demand, providing liquidity at the fund’s net asset value.
Property funds offer numerous benefits, including diversification across various real estate properties and sectors, which helps to mitigate risk. Additionally, these funds are managed by professionals with expertise in real estate, ensuring strategic investment decisions and active asset management.
What is a Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)?
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are companies that own, operate, or finance income-generating real estate across a range of property sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial properties. They provide an accessible way for individual investors to earn a share of the income produced by these properties without the need to buy or manage real estate directly. REITs pool capital from multiple investors to acquire and manage a diverse portfolio of real estate assets, generating income primarily through rent and leasing activities.
There are three main types of REITs:
- Equity REITs own and operate income-producing real estate.
- Mortgage REITs lend money to real estate owners and operators either directly through mortgages and loans or indirectly by acquiring mortgage-backed securities.
Hybrid REITs are a combination of equity and mortgage REITs.
Structure and Organization
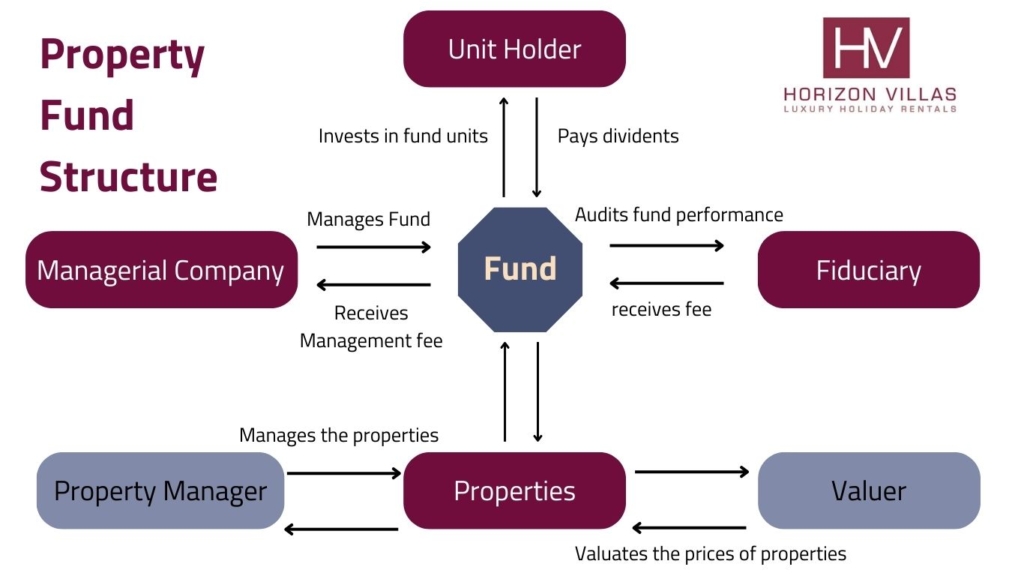
Property Fund
Property Funds can take various forms and structures, with the primary ones being closed-end and open-end funds.
- Investment vehicles: These funds pool investors’ money to invest in a diversified portfolio of properties.
- Types (closed-end vs. open-end): Closed-end funds have a fixed number of shares and typically trade on stock exchanges, while open-end funds issue new shares as investors buy in and redeem shares when they sell.
- Management structure: Typically managed by professional fund managers who make decisions regarding the buying, managing, and selling of properties.
REIT
REITs can be categorized into public, private, and non-traded REITs.
- Public vs. private vs. non-traded REITs: Public REITs are listed on stock exchanges and are highly liquid. Private REITs are not listed and are less liquid, while non-traded REITs are registered with the SEC but do not trade on stock exchanges.
- Legal and regulatory structure: REITs must comply with specific regulations, including distributing at least 90% of taxable income to shareholders.
- Management and governance: Managed by a board of directors or trustees, with day-to-day operations overseen by a team of professionals.
Investment Focus
Property Fund
Property Funds invest in a variety of property types and geographies.
- Types of properties: These can include residential, commercial, industrial, and more.
- Geographic focus: Some funds may focus on specific regions, while others may have a global investment strategy.
REIT
REITs also have diverse investment focuses but are often categorized by property sectors.
- Property sectors: Common sectors include office, retail, healthcare, industrial, and residential properties.
Diversification strategies: REITs often diversify their portfolios across different property types and locations to mitigate risk.
Performance and Returns
For Property Funds, returns are derived from both capital appreciation and income generation. Capital appreciation occurs when the value of the properties owned by the fund increases, while income generation comes from rental income produced by these properties. The performance of a Property Fund is subject to various risk factors, including fluctuations in market conditions, the efficiency of property management, and broader economic trends, all of which can impact both the value and income generated by the properties.
In contrast, REITs are particularly noted for their high dividend yields. This is due to their requirement to distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders as dividends. As a result, REITs often provide attractive income returns, appealing to investors seeking regular income.
Investor Suitability
Property Funds are well-suited for long-term investors who are looking for a combination of capital appreciation and income generation. These funds can be customized to align with various investment goals, whether it’s pursuing high-risk, high-return strategies or focusing on stable income generation. Their flexibility makes them attractive for investors with specific objectives, ranging from growth to steady cash flow.
On the other hand, REITs are ideal for investors seeking regular income and liquidity. They are particularly appealing to income-focused investors due to their high dividend yields, offering a reliable stream of income while allowing for easy buying and selling on stock exchanges. This makes REITs a popular choice for those prioritizing income generation and liquidity in their investment portfolio.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between Property Funds and REITs is essential for investors looking to diversify their portfolios with real estate investments. Property Funds offer diversified property investments with potential for capital appreciation and income generation, while REITs provide high liquidity and regular income through dividends. When choosing between the two, investors should consider factors such as investment goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs. As the real estate market evolves, staying informed about future trends and developments will be crucial for successful investing.