- Home
- Buy
- Rent Discover the ideal rental property in Koh Samui, a tropical haven that offers more than just stunning beaches and clear blue skies. Our comprehensive listings include a diverse selection of properties for rent, from modern apartments in bustling neighborhoods to secluded villas with breathtaking ocean views. Whether you’re planning a short vacation or looking for a long-term stay, Koh Samui has a multitude of rental options to suit your needs and lifestyle. Explore our Koh Samui properties for rent and find your home away from home in this island paradise.
- Developments
- Construction
- Property Management
- Invest
- Information
- THB
- USD
- EUR
- JPY
- CNY
- AUD
- CAD
- GBP
- HKD
- CHF
- Square Feet
- Square Meters
Luxury Villas & Property for Sale and Rent in Koh Samui, Thailand
Understanding Thai Title Deeds
Navigating the intricacies of property ownership in Thailand can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding title deeds. These crucial documents not only establish legal ownership but also determine the rights and restrictions associated with a property. This article will guide you through the various types of Thai title deeds, their importance, and how to verify their authenticity. Additionally, it will explain the process of transferring a title deed, ensuring you are well-equipped for any real estate transaction in this beautiful country.
What is a Title Deed?
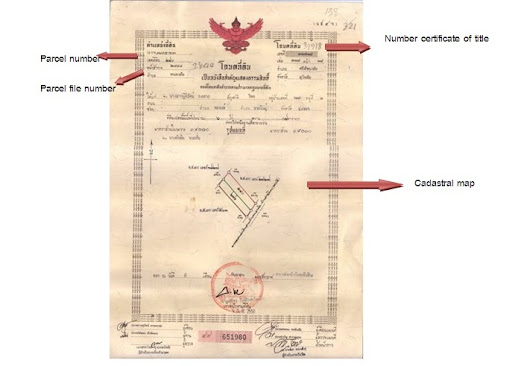
A title deed is a legal document that serves as evidence of property ownership, detailing the rights and interests of the holder in accordance with the local laws. In Thailand, title deeds are crucial for property transactions, listing essential information such as the property’s location, size, and any encumbrances. This document is critical for both residential and commercial properties, ensuring that property rights are protected under Thai law. Understanding the various types of title deeds is vital for anyone looking to buy or invest in property in Thailand. For more details on how to buy properties, click here.
Within the realm of property transactions, the title deed not only confirms ownership but also outlines vital legal components such as land registration, the specific rights granted to the owner, and any obligations tied to the property.
- The deed typically includes a unique identification number.
- It may feature maps or surveys that depict the property’s boundaries.
- Any pending liens or encumbrances are documented to inform prospective buyers.
This clarity helps avoid future disputes and reinforces the importance of reviewing title deeds thoroughly before finalising any property deal. Familiarity with different types of deeds, such as freehold and leasehold, enables buyers to navigate the complexities of property in Thailand more confidently.
Why is a Title Deed Important in Thailand?
The importance of a title deed in Thailand cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in establishing and protecting property rights. In a country where foreign ownership of land can be complex, having a clear and valid title deed is essential for ensuring that the property can be legally owned, transferred, and valued. It serves as a safeguard against property disputes and ensures compliance with Thai law, particularly in land registration processes. Understanding the implications of different title deeds can greatly impact investment decisions, whether for residential, commercial, or investment property.
Title deeds are pivotal in maintaining the integrity of property ownership and are often a first consideration for both local and foreign investors. They provide legally recognised proof of ownership, which is fundamental in securing financing and facilitating smooth property transactions. According to Thai law, these documents help prevent unauthorised claims and protect against any potential legal challenges.
- Legal Protection: A well-documented title deed reduces risks associated with property investments.
- Compliance: Understanding title deeds ensures adherence to Thai land management laws.
- Impact on Foreign Ownership: Certain title deeds can restrict or allow foreign ownership, significantly influencing investment strategies.
As such, being informed about the types and details of title deeds is invaluable for making sound investment choices.
Types of Thai Title Deeds
Understanding the different types of Thai title deeds is essential for anyone looking to invest in real estate in Thailand, as each type comes with its own set of rights and restrictions.
The two most common title deeds are Chanote (Nor Sor 4 Jor), which offers full ownership rights, and Nor Sor 3 Gor, which allows for some level of ownership but may come with conditions.
Other types like Sor Kor 1 and various Por Tor Bor 5 designs serve specific purposes and offer varying degrees of property rights. Knowing which title deed corresponds to your property can guide decisions regarding property ownership, land use, and investment strategies.
Sor Kor Nung (S.K.1)
S.K.1 is the most basic form of land claim in Thailand.
- What it means: You’re basically saying, “Hey, I’m using this land!”
- Rights: You can occupy and use the land, usually for farming.
- Limitations: It’s not much in terms of legal rights. Someone actually farming the land might have a stronger claim than you.
- Transferability: You can sell it or pass it down, but it’s more like handing over your sticky note and hoping the next person’s claim sticks.
- Upgrade potential: In some cases, you might be able to level up to a better title, but it’s getting harder these days.
Fun fact: The government stopped issuing these in 1972, so if you see one, it’s a real blast from the past!
Nor Sor Song (N.S.2)
Think of this as a temporary pass to an exclusive club. You’re in, but you’ve got to follow the rules!
- What it means: The land department is giving you permission to use the land… for now.
- Time limits: You’ve got to start using the land within 6 months and make the most of it within 3 years.
- Transferability: No selling allowed! The only way to transfer is by passing it down in the family.
- Upgrade potential: You might be able to upgrade to a better title, but even then, you still can’t sell it.
Pro tip: If you’re looking at N.S.2 land, make sure you’re ready to commit to using it pronto!
Nor Sor Saam (N.S.3)
This is like having a VIP pass, but the bouncer might still question you at the door.
- What it means: You have the right to possess and use the land as an owner would.
- Boundaries: Here’s the tricky part – the borders are a bit fuzzy. There are no concrete markers showing exactly where your land ends and the neighbor’s begins.
- Legal recognition: This title is recognized by law and can be used as evidence in disputes.
- Usage rights: You can build on it (with proper permits), sell it, or lease it.
- Selling process: There’s a 30-day public notice period when selling. It’s like saying, “I’m selling this land. Any objections?”
- Potential issues: Because the boundaries aren’t clear, you might run into disputes with neighbors or face claims from squatters.
Word to the wise: Always get a proper survey done before buying N.S.3 land to avoid future headaches!
Nor Sor Saam Gor (N.S.3.G)
This is where things start getting serious. It’s like N.S.3 went to college and came back with a fancy degree.
- What it means: You have clear possession rights, and the land has been accurately surveyed.
- Boundaries: The borders are defined using aerial surveys. No more guessing games with your neighbors!
- Selling process: No need for that 30-day waiting period when selling. It’s much smoother sailing.
- Flexibility: You can register various rights against the land (like mortgages) and even subdivide it into smaller plots.
Pro tip: If you’re choosing between N.S.3 and N.S.3.G, go for the G! It’ll save you a lot of potential trouble down the road.
Nor Sor Saam Khor (N.S.3.K)
Think of this as the twin of N.S.3.G, but instead of using aerial surveys, they sent out a team with measuring tapes.
- What it means: Clear possession rights with accurately surveyed boundaries.
- Survey method: Unlike N.S.3.G, this one doesn’t use aerial survey points. It’s all done on the ground.
- Usage: No restrictions on how you use the land.
- Transferability: Like N.S.3.G, there’s no need to announce when you’re selling.
- Flexibility: You can subdivide the land into smaller plots if you want.
Insider info: N.S.3.K is often issued in areas where aerial surveys haven’t been conducted yet.
Chanote (N.S.4.J)
If land titles were a royal family, Chanote would be the king. It’s the gold standard, the cream of the crop!
- What it means: Full, undisputed ownership. This is as good as it gets in Thailand.
- Boundaries: Precisely mapped using GPS. Each corner of your land has a numbered concrete marker.
- Legal strength: Highest level of security and rights. It’s your land, period.
- Flexibility: You can sell, lease, mortgage, or subdivide without restrictions.
- Location: Usually found in more developed areas of Thailand.
- Selling process: Smooth and straightforward. No waiting periods or public notices needed.
Nor Sor Ha (N.S.5)
Imagine you’re in a talent show, and N.S.5 is like having a ticket to perform. But to win the prize, you need to show you’ve actually got talent!
- What it means: This document says you have rights to the land, but it’s not the whole story.
- The sidekick – Utilization Certificate: This is your proof that you’ve actually been using the land productively.
- With the dynamic duo: If you have both the N.S.5 and the Utilization Certificate, you’re golden! It’s like having both the ticket and a standing ovation. You can sell or transfer the land by registering at the land office.
- Flying solo: If you only have the N.S.5 without the Utilization Certificate, it’s like having a ticket but never performing. You can’t sell or transfer the land, except by passing it down in the family.
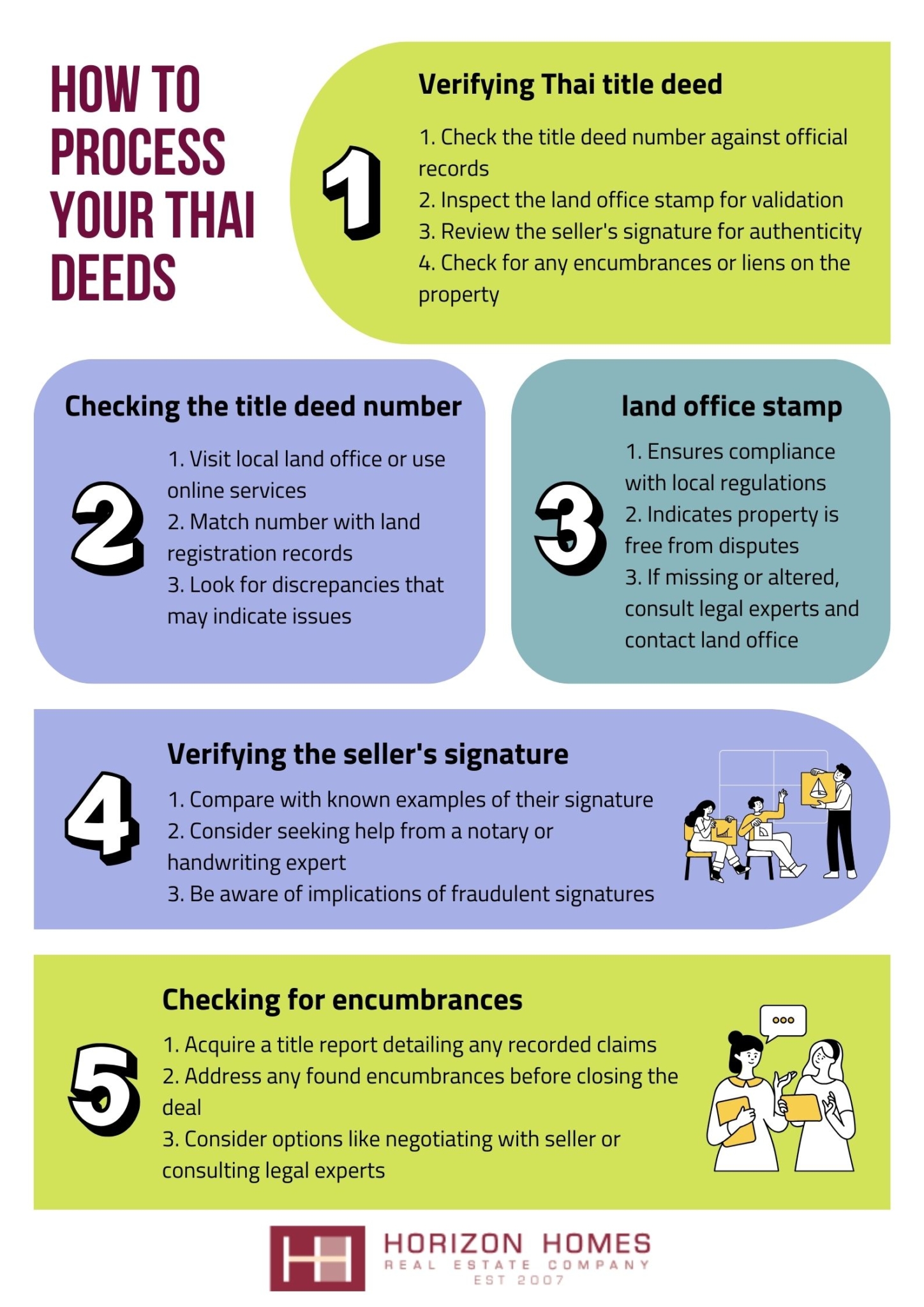
How to Verify the Authenticity of a Thai Title Deed
Verifying the authenticity of a Thai title deed is a critical step for potential property buyers and investors, ensuring that the title is legitimate and that property rights are protected.
This process involves several key steps, including:
- Checking the title deed number against official records,
- Inspecting the land office stamp for validation,
- Reviewing the seller’s signature for authenticity.
By conducting thorough title verification, you can prevent potential property disputes and ensure compliance with Thai law, thus securing your investment in both residential and commercial properties.
The first step in verifying the authenticity of a Thai title deed is to check the title deed number against official land registration records to ensure that the document is valid.
This verification process is crucial for anyone considering purchasing property in Thailand. The title deed number serves as a unique identifier that links the document to the government records, ensuring that the ownership details are accurately reflected. To perform this check, one can visit a local land office or utilise the online services provided by the Thai Land Department.
Matching this number with land registration records not only confirms ownership but also reveals any potential encumbrances or disputes regarding the property. Discrepancies between the title deed and the official records may indicate issues such as fraudulent claims or conflicting ownership claims, which could lead to legal complications down the line. Therefore, it is essential for prospective buyers to be vigilant and ensure that all details align perfectly.
- Visit the local land office for information.
- Utilise online services for convenience.
- Consult with legal experts if discrepancies are found.
Another critical aspect of title verification is checking for the land office stamp, which serves as an official validation of the title deed.
This stamp not only signifies the authenticity of ownership but also indicates that the property has complied with local regulations and is free from disputes. The presence of a valid land office stamp assures prospective buyers and investors of the legitimacy of the title, fostering trust in the transaction.
If the stamp is missing or appears altered, it raises significant red flags. In such instances, one should take the following steps:
- Consult legal experts familiar with property law.
- Request documentation to verify the title’s history.
- Contact the land office for clarification and potential rectification.
Addressing these concerns promptly can prevent future complications and protect one’s investment.
The seller’s signature on the title deed must be examined for authenticity, as this confirms that the individual has the legal authority to sell the property. Ensuring the signature is genuine protects both the buyer and seller from potential disputes.
To verify the seller’s signature, compare it with known examples of their signature, such as from previous documents or public records. It is also advisable to seek professional help from a notary or a handwriting expert who can provide an impartial assessment.
If there are concerns about the authenticity of the signature, consider the following implications of a fraudulent signature:
- Legal disputes which can arise, leading to loss of ownership or costly legal battles.
- Potential financial losses due to invalid contracts or transactions.
- Impact on future property transactions as it may damage credibility.
In the case of suspected forgery, it is crucial to take immediate steps:
- Contact local law enforcement to report the suspected fraud.
- Consult with a solicitor to understand the next course of action.
- Gather and preserve any relevant documentation that supports your concerns.
By addressing these issues promptly, both parties can navigate the complexities of property transactions with greater confidence.
It’s essential to check for any encumbrances or liens on the property, as these can impact ownership rights and the ability to transfer property freely. Ahead of finalising any property transaction, it is crucial to thoroughly investigate the title for any potential claims, ensuring that you are aware of any financial obligations attached to the property in question.
Begin by acquiring a title report, which will detail any recorded liens or claims against the property. This report serves as a critical document, offering insights into:
- Outstanding mortgages
- Judgments from lawsuits
- Tax liens
- Mechanic’s liens for unpaid work
If an encumbrance is found, it is vital to address it prior to closing the deal. Options include:
- Negotiating with the seller to clear the lien
- Establishing an escrow account to cover potential payments
- Consulting a legal expert to navigate the complexities of resolving liens
Taking these steps can prevent disruptions and safeguard ownership rights during the transaction process.
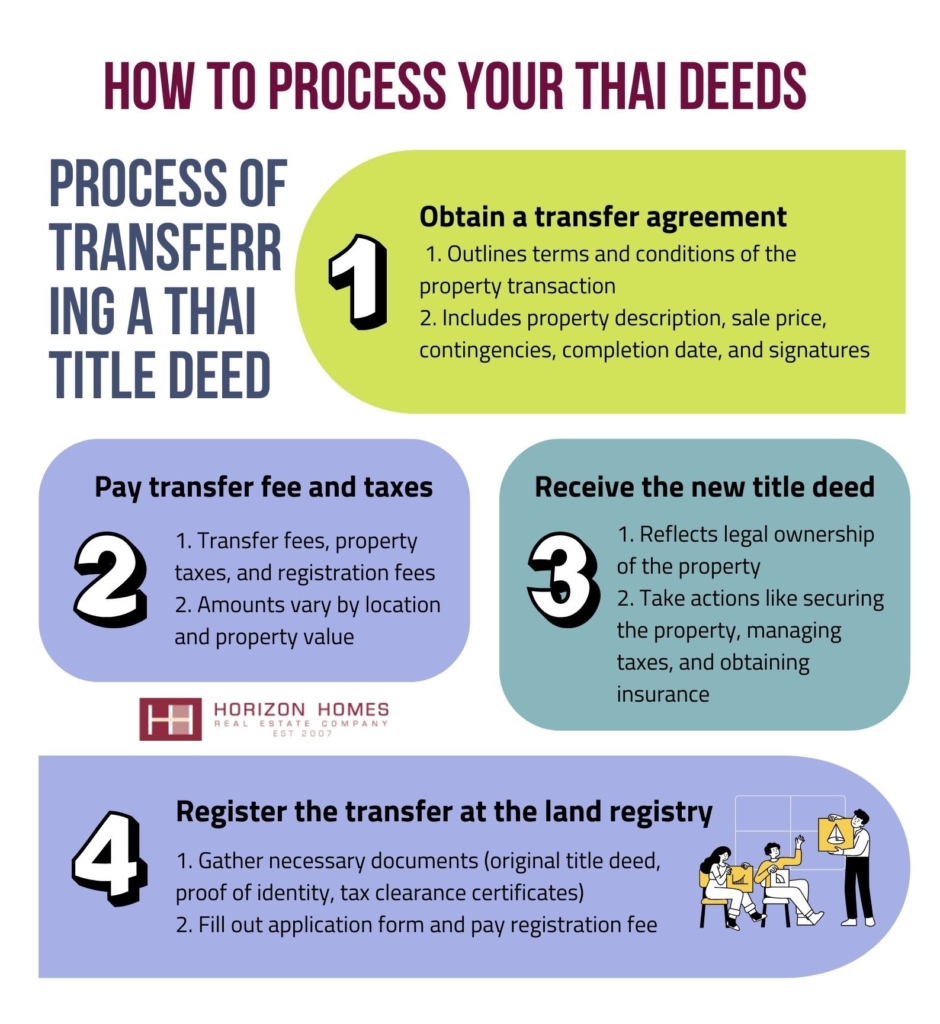
The Process of Transferring a Thai Title Deed
Transferring a Thai title deed is a multi-step process that requires careful attention to legal details, as it involves both property taxes and completion costs.
The process begins with obtaining a transfer agreement, which outlines the terms of the property transfer and the responsibilities of each party. Once this is completed, the transfer must be registered at the land registry, where the new title deed will be issued to the buyer.
This process is crucial for ensuring that property rights are legally recognized and protected under Thai law, making it an essential step for any investment in residential or commercial property.
The first step in the title deed transfer process is to obtain a transfer agreement, which serves as a legal document outlining the terms and conditions of the property transaction.
A transfer agreement encompasses various essential elements that ensure transparency and security for both parties involved. This document is vital not only for clarifying the specifics of the deal but also for protecting the legal rights of the buyer and seller. Key components often include:
- Property Description: A detailed account of the property being transferred, including boundaries and any structures.
- Sale Price: The agreed amount that the buyer will pay for the property.
- Contingencies: Conditions that must be met for the transaction to proceed, such as inspections or financing.
- Completion Date: The timeline for finalising the transfer.
- Signatures: Both parties must sign the agreement to validate their consent and commitment.
By including these elements, the transfer agreement acts as a fundamental safeguard that minimises disputes and clarifies expectations, ultimately fostering a smooth transaction process.
After obtaining the transfer agreement, the next step is to pay the required transfer fee and any applicable property taxes, which are essential for successful land registration.
These financial obligations, including various fees and taxes, often vary by location and can significantly influence the total cost of property ownership. For instance, the transfer fee is typically a percentage of the property’s value, while property taxes are calculated based on assessed value and local tax rates. It’s important to understand these components:
- Transfer Fees: Often a set percentage charged by the government when ownership of the property changes hands.
- Property Taxes: Annual taxes based on the assessed value, which can vary by jurisdiction.
- Registration Fees: Fees incurred for the public recording of the property transfer.
Neglecting to pay these dues can result in penalties, including interest charges and potential legal action, ultimately complicating the registration process.
The registration of the transfer at the land registry is a crucial step that finalises the transfer of the title deed and legally recognises the new owner’s property rights.
To ensure a smooth transition, the new owner must gather several important documents, including the original title deed, proof of identity, and any applicable tax clearance certificates. Completing this registration process not only legitimises the transfer but also protects the new owner’s interests from future disputes or claims.
The process typically involves filling out an application form, paying a registration fee, and possibly undergoing a verification process where details are cross-checked against official records.
- Original Title Deed
- Proof of Identity
- Tax Clearance Certificate
This crucial step not only secures ownership but also sets a firm foundation for any future dealings concerning the property.
Once the transfer is registered at the land registry, the new owner will receive the updated title deed, which reflects their legal ownership of the property and grants them essential rights concerning the enjoyment and control of their newly acquired asset.
This updated title deed plays a pivotal role in establishing the new owner’s rights and responsibilities, ensuring protection against disputes and establishing their claim against any third parties. After obtaining this important document, there are several key actions to consider:
- Secure the Property: It is advisable to change the locks and enhance security features to safeguard the property from unauthorised access.
- Manage Taxes: The owner should reach out to the local tax authority to understand property tax obligations and deadlines, avoiding any future complications.
- Insurance: Obtaining a home insurance policy will provide financial protection against potential damages and liabilities.
By taking these critical steps, the new owner not only fortifies their investment but also ensures compliance with local regulations and financial responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Thai title deeds?
Thai title deeds are official documents that prove ownership of land or property in Thailand. These deeds are issued by the Thai government and are essential for legal ownership of real estate in the country.
What are the different types of Thai title deeds?
There are four main types of Thai title deeds: Chanote, Nor Sor Sam Gor, Nor Sor Sam, and Sor Kor Nung. Chanote is the most secure and recognized type of title deed, while Sor Kor Nung is the least secure and only grants temporary ownership rights.
How do I check the validity of a Thai title deed?
You can verify the validity of a Thai title deed by checking with the local Land Office or hiring a reputable lawyer to conduct a thorough title search. It is essential to ensure that the title deed is legitimate before purchasing any property in Thailand.
What information is included in a Thai title deed?
A Thai title deed typically includes information such as the owner’s name, location and size of the property, and any encumbrances or restrictions on the property. It also includes a map of the land and its boundaries.
Why is it important to understand Thai title deeds?
Understanding Thai title deeds is crucial for anyone looking to purchase property in Thailand. It ensures that the property you are buying has a legitimate and secure title, avoiding any legal issues or disputes in the future.
Can foreigners own property in Thailand?
Yes, foreigners can own property in Thailand, but there are certain restrictions. Foreigners cannot own land in their name but can own buildings and structures on the land. They can also own condominium units as long as 51% of the building is owned by Thai citizens.